Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMRHGI9)
| Drug Name |
Cisplatin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Abiplatin; Biocisplatinum; Briplatin; Cismaplat; Cisplatine; Cisplatino; Cisplatinum; Cisplatyl; Citoplationo; Lederplatin; Neoplatin; Plastin; Platamine; Platidiam; Platinoxan; Randa; Cis-DDP; Cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum; Peyrone's chloride; Peyrone's salt; Cis-Dichlorodiammineplatinum(II); Cis-[PtCl2(NH3)2]; Cis-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II); Trans-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II); (SP-4-1)-diamminedichloridoplatinum; (SP-4-1)-diamminedichloroplatinum; (SP-4-2)-diamminedichloridoplatinum; (SP-4-2)-diamminedichloroplatinum; Cisplatin (Chemotherapy)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
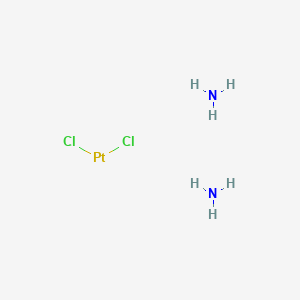 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL is unavailable | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 |
Molecular Weight | 300.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Cisplatin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Cisplatin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5343). | ||||
| 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Genome-wide association study of chemotherapeutic agent-induced severe neutropenia/leucopenia for patients in Biobank Japan. Cancer Sci. 2013 Aug;104(8):1074-82. doi: 10.1111/cas.12186. Epub 2013 Jun 10. | ||||
| 9 | Megalin genetic polymorphisms and individual sensitivity to the ototoxic effect of cisplatin. Pharmacogenomics J. 2008 Feb;8(1):23-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500455. Epub 2007 Apr 24. | ||||
| 10 | Cisplatin and DNA repair in cancer chemotherapy.Trends Biochem Sci.1995 Oct;20(10):435-9. | ||||
| 11 | Overcoming platinum drug resistance with copper-lowering agents. Anticancer Res. 2013 Oct;33(10):4157-61. | ||||
| 12 | Effect of cisplatin on the transport activity of PII-type ATPases. Metallomics. 2017 Jul 19;9(7):960-968. | ||||
| 13 | Characterization of the drug resistance and transport properties of multidrug resistance protein 6 (MRP6, ABCC6). Cancer Res. 2002 Nov 1;62(21):6172-7. | ||||
| 14 | Copper transporter 2 regulates endocytosis and controls tumor growth and sensitivity to cisplatin in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Jan;79(1):157-66. | ||||
| 15 | Lentivirus-mediated RNAi silencing targeting ABCC2 increasing the sensitivity of a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line against cisplatin. J Transl Med. 2008 Oct 4;6:55. | ||||
| 16 | Cisplatin and oxaliplatin, but not carboplatin and nedaplatin, are substrates for human organic cation transporters (SLC22A1-3 and multidrug and toxin extrusion family). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Nov;319(2):879-86. | ||||
| 17 | Hammerhead ribozyme against gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase sensitizes human colonic cancer cells to cisplatin by down-regulating both the glutathione synthesis and the expression of multidrug resistance proteins. Cancer Gene Ther. 2001 Oct;8(10):803-14. | ||||
| 18 | Inhibiting the function of ABCB1 and ABCG2 by the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Mar 1;77(5):781-93. | ||||
| 19 | Cisplatin nephrotoxicity is critically mediated via the human organic cation transporter 2. Am J Pathol. 2005 Dec;167(6):1477-84. | ||||
| 20 | Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016 Jan 1;370(1):153-64. | ||||
| 21 | Cytochrome P450 2E1 null mice provide novel protection against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and apoptosis. Kidney Int. 2003 May;63(5):1687-96. | ||||
| 22 | Role of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 in the cellular detoxification of cisplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):3247-55. | ||||
| 23 | PharmGKB: A worldwide resource for pharmacogenomic information. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2018 Jul;10(4):e1417. (ID: PA150642262) | ||||
| 24 | Glutathione S-transferase genetic polymorphisms and individual sensitivity to the ototoxic effect of cisplatin. Anticancer Drugs. 2000 Sep;11(8):639-43. | ||||
| 25 | Role of metallothionein in cisplatin sensitivity of germ-cell tumours. Int J Cancer. 2000 Mar 15;85(6):777-81. | ||||
| 26 | Cisplatin reduces Brucella melitensis-infected cell number by inducing apoptosis, oxidant and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Res Vet Sci. 2010 Apr;88(2):218-26. | ||||
| 27 | GSTA4 mediates reduction of cisplatin ototoxicity in female mice. Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 12;10(1):4150. | ||||
| 28 | Activation of AIFM2 enhances apoptosis of human lung cancer cells undergoing toxicological stress. Toxicol Lett. 2016 Sep 6;258:227-236. | ||||
| 29 | Characterisation of cisplatin-induced transcriptomics responses in primary mouse hepatocytes, HepG2 cells and mouse embryonic stem cells shows conservation of regulating transcription factor networks. Mutagenesis. 2014 Jan;29(1):17-26. | ||||
| 30 | Low doses of cisplatin induce gene alterations, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Biomark Insights. 2016 Aug 24;11:113-21. | ||||
| 31 | Acute hypersensitivity of pluripotent testicular cancer-derived embryonal carcinoma to low-dose 5-aza deoxycytidine is associated with global DNA Damage-associated p53 activation, anti-pluripotency and DNA demethylation. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053003. Epub 2012 Dec 27. | ||||
| 32 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 33 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 35 | Johnson EJ, MacGowan AP, Potter MN, et al "Reduced absorption of oral ciprofloxacin after chemotherapy for haematological malignancy." J Antimicrob Chemother 25 (1990): 837-42. [PMID: 2373666] | ||||
| 36 | FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Low magnesium levels can be associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitor drugs (PPIs).". | ||||
| 37 | Chang JT, Green L, Beitz J "Renal failure with the use of zoledronic acid." N Engl J Med 349 (2003): 1676-9 discussion 1676-9. [PMID: 14573746] | ||||
| 38 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Edecrin (ethacrynic acid). Merck & Co, Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 40 | Komune S, Snow JB "Potentiating effects of cisplatin and ethacrynic acid in ototoxicity." Arch Otolaryngol 107 (1981): 594-7. [PMID: 7197152] | ||||
| 41 | Carrion C, Espinosa E, Herrero A, Garcia B "Possible vincristine-isoniazid interaction." Ann Pharmacother 29 (1995): 201. [PMID: 7756727] | ||||
| 42 | Argov Z, Mastaglia FL "Drug-induced peripheral neuropathies." Br Med J 1 (1979): 663-6. [PMID: 219931] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 44 | Markman M, Trump DL "Nephrotoxicity with cisplatin and antihypertensive medications." Ann Intern Med 96 (1982): 257. [PMID: 7199267] | ||||
| 45 | Novis BH, Korzets Z, Chen P, Bernheim J "Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296 (1988): 1442. [PMID: 3132281] | ||||
| 46 | Banerjee D, Asif A, Striker L, Preston RA, Bourgoignie JJ, Roth D "Short-term, high-dose pamidronate-induced acute tubular necrosis: The postulated mechanisms of bisphosphonate nephrotoxicity." Am J Kidney Dis 41 (2003): E18. [PMID: 12778436] | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Prolia (denosumab). Amgen USA, Thousand Oaks, CA. | ||||
| 48 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 51 | Bennett CL, Nebeker JR, Samore MH, et al "The Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports (RADAR) project." JAMA 293 (2005): 2131-40. [PMID: 15870417] | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Vumerity (diroximel fumarate). Alkermes, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Ocrevus (ocrelizumab). Genentech, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Synribo (omacetaxine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 56 | Cohen J "Long-term efficacy and safety of terazosin alone and in combination with other antihypertensive agents." Am Heart J 122 (1991): 919-25. [PMID: 1678923] | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Alimta (pemetrexed). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 58 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Arcalyst (rilonacept). Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc, Tarrytown, NY. | ||||
| 60 | Product Information. Cimzia (certolizumab). UCB Pharma Inc, Smyrna, GA. | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Orap Tablets (pimozide). Gate Pharmaceuticals, Sellersville, PA. | ||||
| 62 | CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/ "Recommendations of the advisory committtee on immunization practices (ACIP): use of vaccines and immune globulins in persons with altered immunocompetence." MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 42(RR-04) (1993): 1-18. [PMID: 20300058] | ||||
| 63 | Antonelli D, Atar S, Freedberg NA, Rosenfeld T "Torsade de pointes in patients on chronic amiodarone treatment: contributing factors and drug interactions." Isr Med Assoc J 7 (2005): 163-5. [PMID: 15792261] | ||||
